- 2-minute read
- 31st May 2018
Microsoft Word Tips: Using Columns
In most documents, text is formatted in paragraphs that spread across the page. But this doesn’t have to be the case: you can use columns instead. These are especially common in newspapers, newsletters and magazines, but you will also find them in academic journals and other periodicals.
Why do people use this formatting in writing, though? And how does this work in Microsoft Word?
When to Use Columns

Readability is essential in all writing. Proofreading and editing your document will help with this, but presentation is also a factor. The columns in newspapers and magazines are a great example of this.
The simple fact is that shorter lines are easier to read (the optimal length is around 60 characters). Using columns therefore helps to break up the text so that no line is too long. This is also why they are more common in newspapers and magazines than books, which usually have narrower pages.
If, then, you are printing something A4 size or above, you may want to format it in columns.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Formatting in Microsoft Word
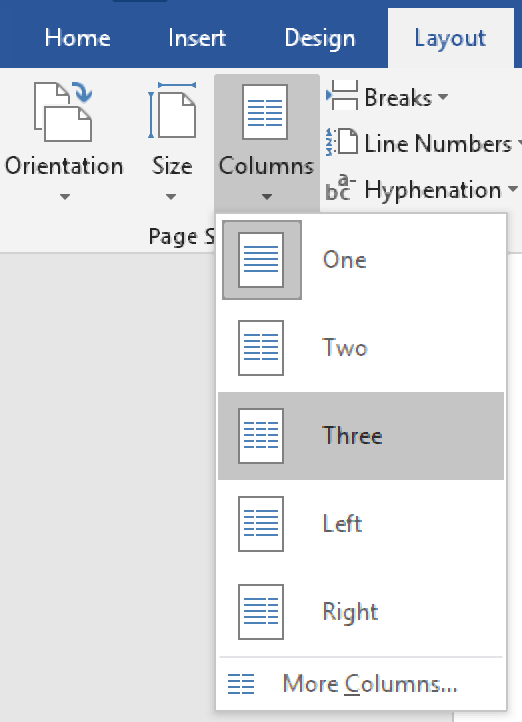
To format existing text, all you need to do is:
- Select the text you want to format
- Go to Layout > Page Setup on the ribbon
- Click Columns and select the number and style of columns required
This will apply your chosen formatting to the selected text. The options in the dropdown menu here are fairly basic, but you will rarely need more than three columns on a single page.
However, if you do want more control over column formatting, click More Columns… in the dropdown menu. This will open a new window. The options here let you control:
- The number required per page
- Whether to add a line between columns
- Individual column width
- Which parts of the document you want to format
This final option will automatically insert a section break in your document if you select This point forward from the menu. Keep this in mind if you later apply other formatting to the document, such as page numbers, as it may only be applied to the currently selected sections.